

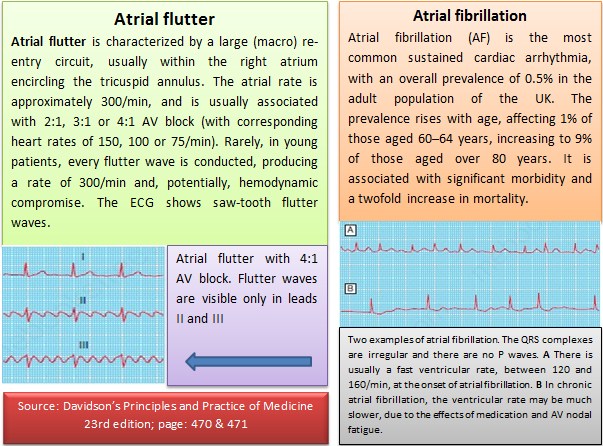
Atypical Aflutter may have varying AV conduction, which can cause an irregular heart rhythm. ‘Coarse Afib’ has an “f” wave amplitude> 0.5 mm, which can mimic Aflutter “f” waves morphology. It may be difficult to distinguish atypical Aflutter from coarse Afib. Atrial flutter or atrial fibrillation with junctional rhythm is the combination of rapid regular (atrial flutter) or rapid irregularly irregular (atrial. Heart rate ” Irregularly irregular” and variable (slow Afib 100 bpm)įig.2 Atrial fibrillation ECG (with Ashmann phenomenon)ĭistinguish atypical Aflutter from coarse Afib: Atrial fibrillation/flutter (atrial fibrillation and flutter are abnormal heart rhythms in which the atria, or upper chambers of the heart, are out of sync with the ventricles) is found to be associated with 3,741 drugs and 3,563 conditions by eHealthMe. One major difference is that patients with atrial flutter can still sometimes have a regular pulse rate while the pulse is always irregular with AFib.Atypical (type II) atrial flutter: doesn’t fulfill the criteria for typical atrial flutter.Clockwise: positive flutter waves in II, III, aVF and negative in V1.Counterclockwise: negative flutter waves in II, III, aVF and positive in V1.Typical (type I) atrial flutter: saw-tooth-like waves Atrial fibrillation is commonly associated with other supraventricular arrhythmias, namely atrial flutter and focal atrial tachycardia.300 bpm (200-400 bpm) with a heart rate typically ca. Afib and atypical Aflutter requires more expertise and radiofrequency ablation has lower success rate.Ītrial rate ca. The difference between atrial fibrillation (Afib) and atrial flutter (Aflutter), is clinically relevant because typical flutter can easily be treated by radiofrequency ablation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
